Visiting the sales without selling out the environment
The sales are back and are a wonderful opportunity to bag a bargain whilst pondering our consumption practices. A lot is said about food waste, but textile waste is a worrying reality for biodiversity.
Europeans are buying more and more clothes, with Belgians purchasing between 20 and 25 kilos of clothes a year on average, 60% more than in 2000. And these clothes are not worn much, either because the quality is not as good, or because they quickly become unfashionable. We keep them for half as long as we did at the start of the century! And less than a quarter of these purchases end up being recycled.
This over-consumption of textiles is caused by the huge choice available, and a frantic rotation of the collections on the shelves. Not all clothes find a buyer, and these unsold items are generally destroyed.
First problem: water!
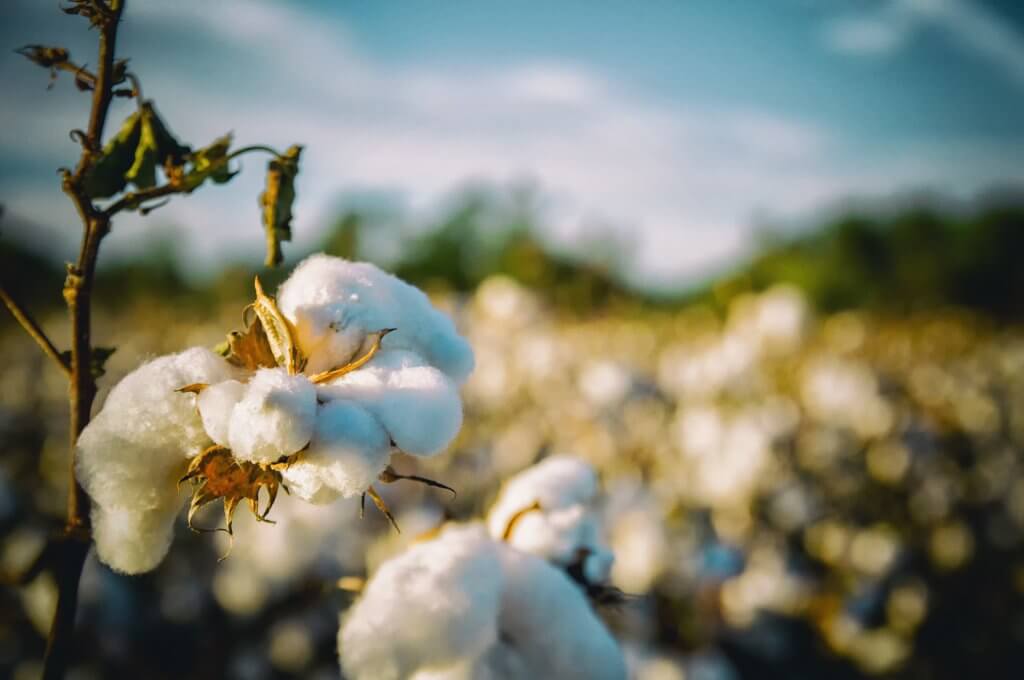
We often forget that textiles are usually made from plants, primarily hemp, linen and cotton. Cotton is used for almost 40% of our clothes! The production of these natural resources affects our biodiversity.
Did you know that it takes 2,700 litres of water to produce one cotton t-shirt, which is what one person drinks in two and a half years? This insatiable thirst can have disastrous consequences for entire ecosystems, as was the case with the drying up of the Aral Sea due to the irrigation of the cotton fields of central Asia.

Second problem: chemicals
The fashion industry also uses a lot of chemicals. It is responsible for around 20% of industrial water pollution at a global level. The production of viscose is particularly damaging. While viscose is of plant origin, it undergoes intense chemical processing that often has a dramatic effect on biodiversity. The viscose industry is responsible for polluting the largest freshwater lake in China; its water is now black and is toxic to both porpoises and humans.
And the icing on the cake: transport
As we buy more and more clothes, they have to travel further and further to reach our wardrobes. More than 60% of clothes are made in South-East Asia and transporting these goods around the world contributes to climate change, which itself is damaging to biodiversity.
In short, buying the latest fashions that will not last is very costly for the species on our planet. So, step this way for a few ideas for responsible shopping.
Actus Associés
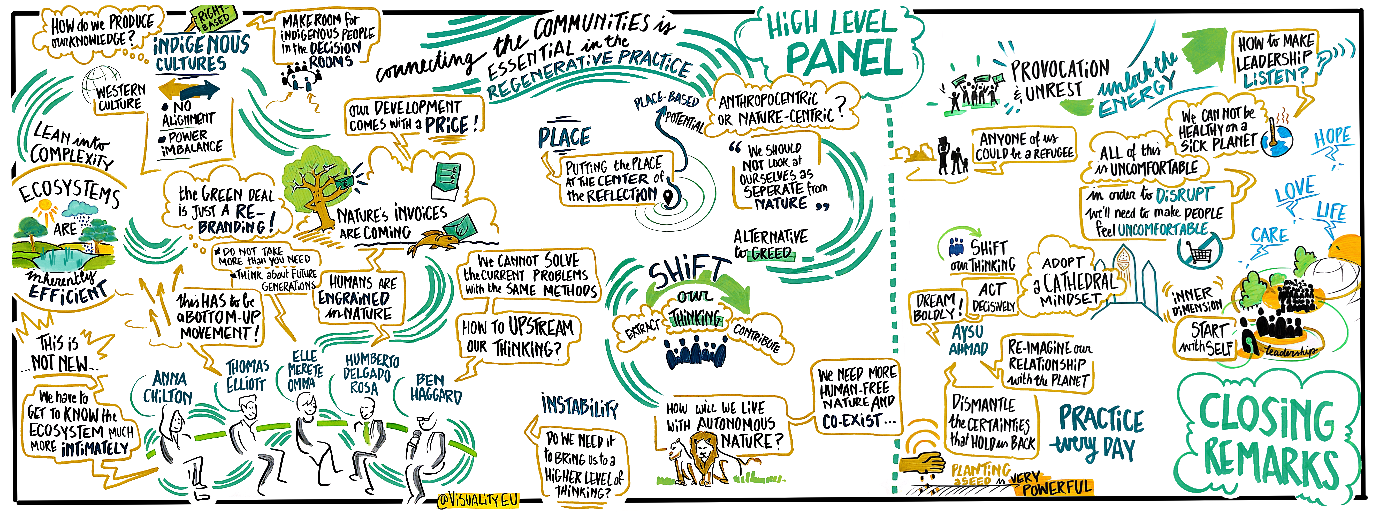
Regenerative development and design: improving governance, innovation and planetary health
Humans have pushed several planetary boundaries out of their safe operating space and inequalities within and between countries are rising… Our current societal and environmental challenges require a meta-response. This is what Regenerative Development and Design (RDD) aims to bring.
See more
Save biodiversity by eating better
Our food choices have significant effects on biodiversity and ecosystems, but also on our health. Among other things, intensive meat production is responsible for the destruction of many ecosystems around the world and excessive meat consumption is a source of various diseases. Yet demand is growing on an increasingly populated planet with limited natural resources. As individuals, do we have a role to play in mitigating this trend in a globalised world? The answer is yes!
See more
A very meaty diet: what consequences for biodiversity?
Did you know that, in the European Union, the food industry is the main cause of environmental damage, followed by housing and mobility?[1] Although many consumers are aware of this, we tend to underestimate the effects of our eating habits on the environment.[2] While this is not good news, it does mean that our choices can make a real difference. But can we really protect biodiversity at mealtimes?
See more





